A sudden blockage of blood flow to the brain due to a clot, causing rapid loss of essential neurological function and severe damage.
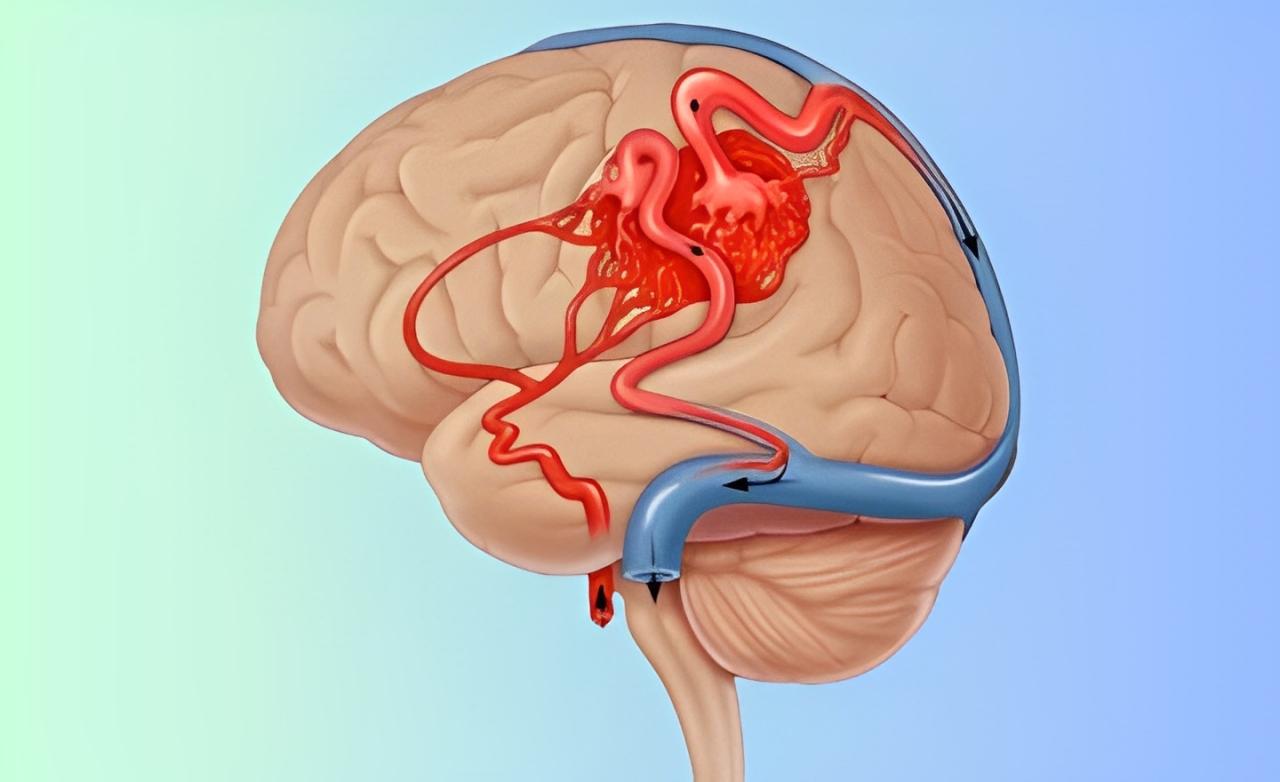
Abnormal tangling of arteries and veins in the brain, disrupting flow, causing headaches, seizures, or hemorrhage.
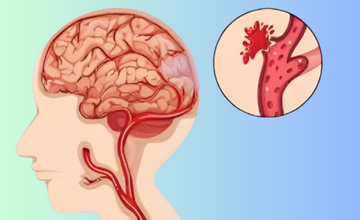
Occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding in or around the brain, leading to pressure and tissue damage.
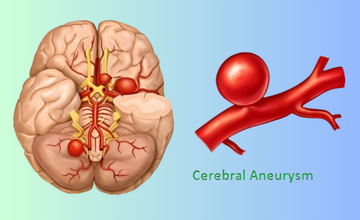
A bulging, weakened blood vessel in the brain that may rupture, causing life-threatening bleeding, headaches, neurological deficits, or stroke.

A minimally invasive procedure injecting bone cement into fractured vertebrae, stabilizing the spine, relieving pain, and restoring mobility in patients.

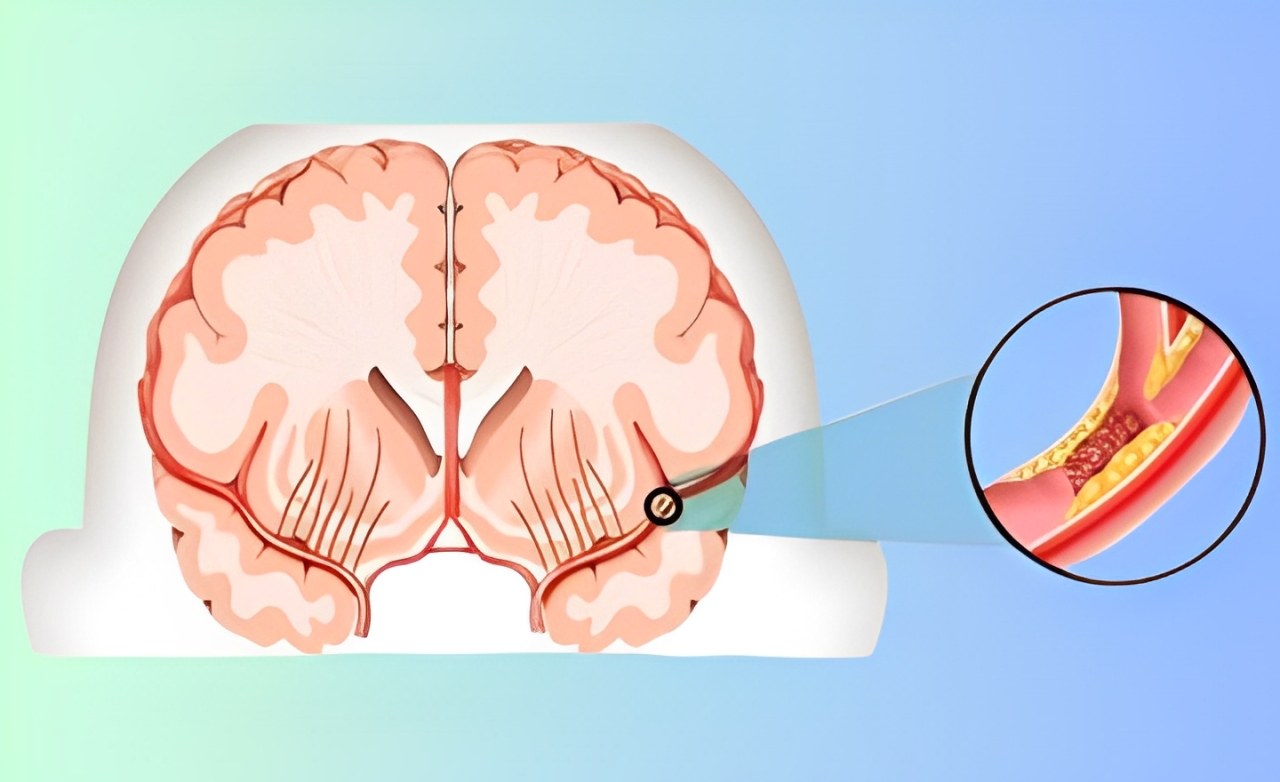
Narrowing of the carotid arteries due to plaque buildup, reducing brain blood flow and increasing risk of transient ischemic attacks.

Bleeding inside or around the brain caused by trauma, hypertension, or aneurysms, resulting in swelling, pressure, and impaired function.

A minimally invasive endovascular procedure removing clots from blocked brain arteries, restoring blood flow, and reducing disability after stroke.

Restores blood flow by removing clots, improving outcomes and reducing disability in acute stroke patients.

Minimally invasive technique using soft coils to block aneurysm flow, preventing rupture and ensuring long-term vascular stability.

Provides support for wide-neck aneurysms, ensuring secure coil placement and safer, more effective treatment.
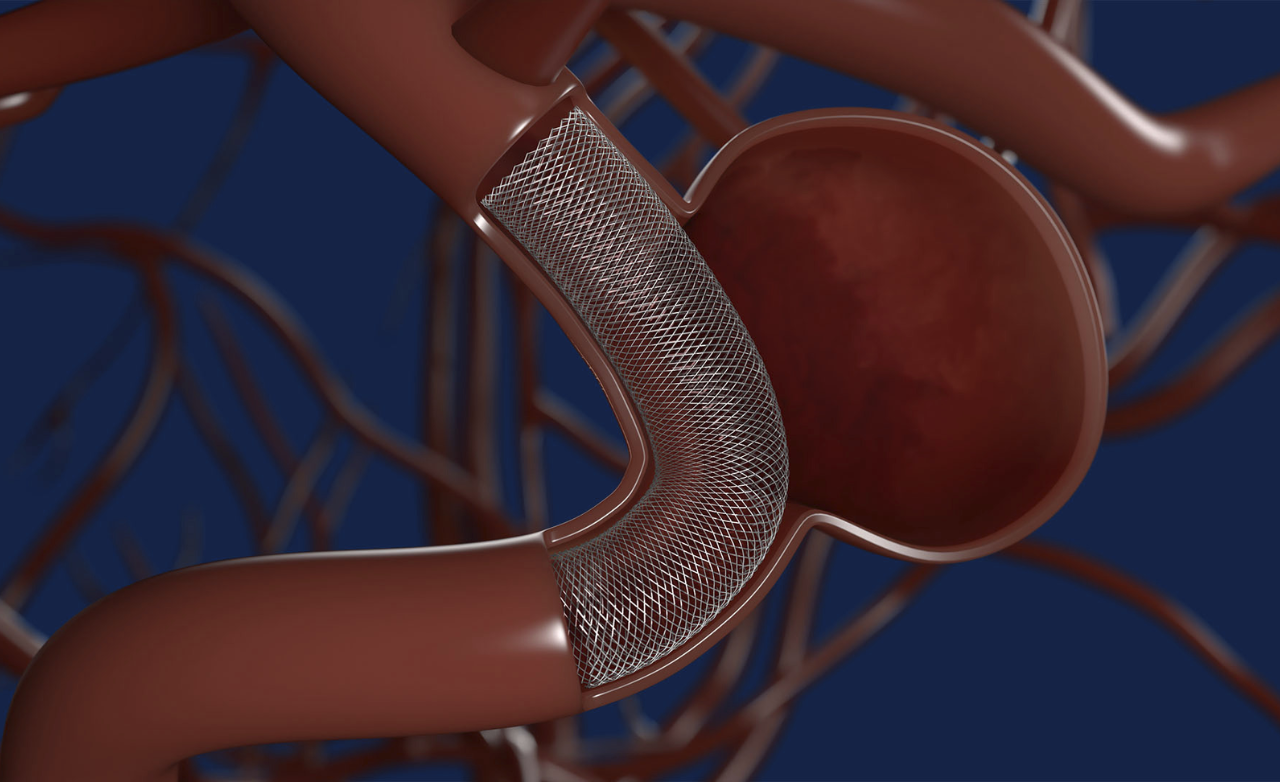
Enhances treatment by redirecting blood flow away from the aneurysm, promoting gradual healing, improving vessel stability, and ensuring stronger, durable protection against future rupture.

Placed directly inside the aneurysm sac, these devices offer targeted treatment with minimal vessel manipulation for improved safety.

Opens narrowed arteries supplying the brain, improving blood flow and reducing stroke risk through a precise, minimally invasive procedure.

Blocks abnormal blood vessel connections to reduce bleeding risks, shrink the malformation, and prepare for further treatment if needed.

Closes abnormal artery-to-dura connections, relieving symptoms & preventing complications through targeted, imageguided vascular treatment.

Treats chronic subdural hematoma by blocking the middle meningeal artery, reducing recurrence and supporting faster, safer recovery.

Restores venous drainage by widening narrowed sinuses, lowering intracranial pressure and symptoms.

Cuts off blood supply to tumors, reducing size, minimizing surgical bleeding, and enhancing overall treatment effectiveness.
Copyright © 2025 Dr. K S V Surya Teja Reddy– All Rights Reserved by Galaxy Tech Solutions